SEQUENTIAL FILES
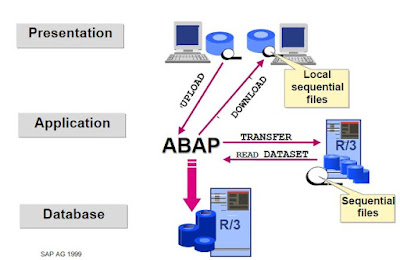
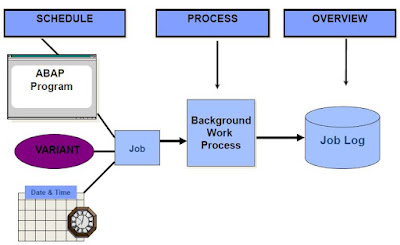
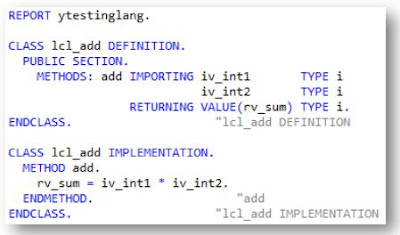
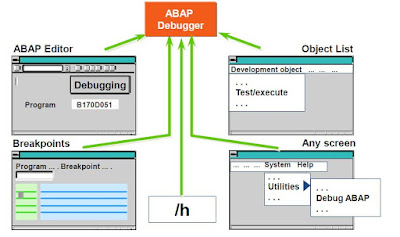
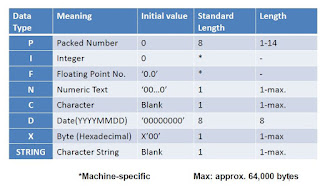
Module Objectives Describe the process of opening and closing files Define binary mode and text mode Define the TRANSFER and READ DATASET statements Define the CLOSE DATASET and DELETE DATASET statements Define ABAP statements to fill the fields of a structure Define the process for reading, extending and creating a file Data Imports and Exports Data imports and exports Processing Files there are three step of File processing. Open file Process file Close file Working with Sequential Files Reading Data OPEN DATASET <file name> FOR INPUT. : : READ <file name> INTO <field>. : : CLOSE DATASET <file name>. Writing Data OPEN DATASET <file name> FOR OUTPUT. : : TRANSFER <field> TO <file name>. : : CLOSE DATASET <file name>. style="display:block" data-ad-format="fluid" data-ad-layout="image-side" data-ad-layout-key="-fg+5r+6h-fn+4k" data-ad-client="ca-pub-4708127434193346...