OOP
OOP
- Understand the details of object-oriented syntax elements in ABAP Objects and use these effectively
- Create object-oriented models of business applications
- Use the tools in the ADT 2.70 to develop object-oriented applications
what problems we were having in Procedural programming.
- Long code due to variable declaration
- Extensive processing after SQL statement
- Multiple Commands to perform simple operations
- Code reusability and Maintenance
SAP’s solution
- In-line declaration
- SQL Expressions
- ABAP Expressions
- OOP
Advantages of OOP over Procedural programming
- Improved software structure and consistency in the development process
- Reduced maintenance efforts and less susceptibility to errors
- Better integration of the customer/user into the analysis, design, and maintenance process
- Easier and safer possibilities for extending the software
OOP in ABAP
- Essentially the same as those of other modern object-oriented languages like C++ or Java
- Some elements present in ABAP objects are not offered in C++ and Java
- Some specific features of ABAP objects only exist because of the guaranteed downward compatibility of older ABAP language elements
OOP Model of ABAP Objects
- ABAP Objects statements can be used in procedural ABAP programs
- Objects (classes) contain procedural ABAP statements
- In the object-oriented context :
- Only object-oriented concepts that have been proven useful
- Increased use of type checks
- Obsolete statements are prohibited
OOP Model of ABAP Objects Example
 |
| OOP Model Of ABAP |
Class and objects
Class:
General Description of Objects
- Specifies status data (attributes) and behavior (methods)
- Example: Person, Employee
Object:
Representation of section of the real world
- Concrete form/specimen/instance of a class
- Example: Xed, Shayne
Attributes
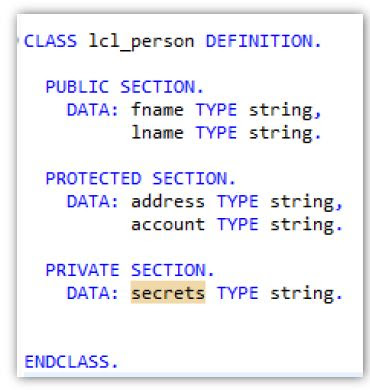
Public Attributes
- Generally Visible
- Generally Changeable
- Exception: READ-ONLY Addition
Protected Attributes
- accessible to all methods of the class and of classes that inherit from it.
Private Attributes
Attributes
Static Attributes
- Exist per class
- Can be called without instantiation
- Definition with CLASS-DATA
Instance Attributes
- Exist per instance
- Can only be called if class is instantiated
- Defined with DATA
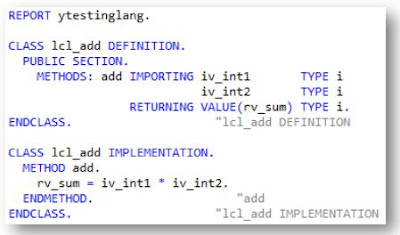
Methods
- Internal procedures in classes that determine the behavior of the objects
- Can access all attributes in their class and can therefore change the state of other elements
- Methods have a signature (interface parameters) that enables them to receive values when they are called and pass back values back to the calling program
 |
| Method |
Interface Parameters
- Can have any number of IMPORTING, EXPORTING, CHANGING, and RETURNING VALUE parameters
- All parameters can be passed by value or reference
- Input parameters can be mandatory or OPTIONAL parameters with a DEFAULT value
 |
| Interface Parameter |
Methods
- Public Methods
Can generally be called outside the class
- Protected Methods
Can be called within the class and subclass.
- Private Methods
Can only be called within the class

Comments
Post a Comment